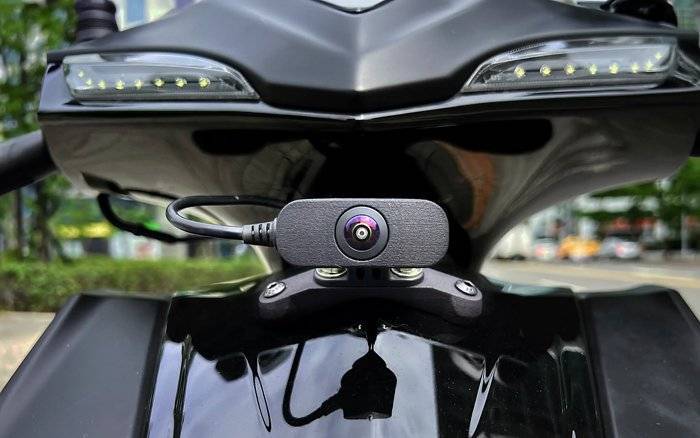
Collision warning systems, which have become an integral part of many modern cars, are, alas, not yet available for bicycles and mopeds. However, thanks to developments by the California-based company Roadio, this could soon change for the better, especially since former employees of Apple, Tesla and Uber were involved.
The system with the same name consists of three components – two front and rear view cameras of “fish-eye” type with a sector of view of 210 degrees each and the RoadioSafety application downloaded to the driver’s smartphone (installed on the steering wheel). The HD cameras provide an all-round view of the road, which is continuously analyzed by computer vision augmented by the app’s AI algorithms.
Advertisement
Technologies
US scientists have learned how to turn carbon dioxide into superstrong nanofibers
Researchers from Brookhaven National Laboratory and Columbia University have proposed a new way to turn carbon emissions into useful material. In their method, carbon dioxide is extracted from the atmosphere and becomes carbon nanofibers, which are hidden for decades in concrete structures as filler for building material. The idea itself is not new, but in this case tandem technology is used, which simplifies and cheapens the process.
In the first step, the mixture of carbon dioxide and water is fed to an electric catalyzer, where it is separated into carbon and hydrogen using a palladium electrode. Both gases are collected in separate containers. The carbon is then fed into a cobalt-nickel alloy thermocatalyst. It is heated to a temperature of only 400° C compared to 1000° C in the classical method, which simplifies the implementation of this process in production.
Near the city of Tucson, Arizona, a metal pole with a special camera on top has been installed. It is designed to capture the changes in the local landscape over thousands of years. This is the creative project of experimental philosopher Jonathan Keats, who expects to install similar cameras in China, the Austrian Alps, U.S. nature reserves and other places.
Keats admits that his project has no artistic, commercial, scientific, or any meaning at all. Moreover, with the probability of 100% it will not be brought to the end, because no one is going to monitor the safety of the installation for the whole 1000 years. If not natural disasters, human activity will surely destroy the pole and the camera.
What matters here is the idea itself, and it is not impossible that it will be picked up and realized in one form or another. The camera on the pole is not digital, it is a camera obscura modeled after the devices of ancient Rome. A tiny hole is made in the 24-karat gold plate, which is weather-resistant. Light passing through it flips and falls on a multilayer photosensitive coating, creating an image.
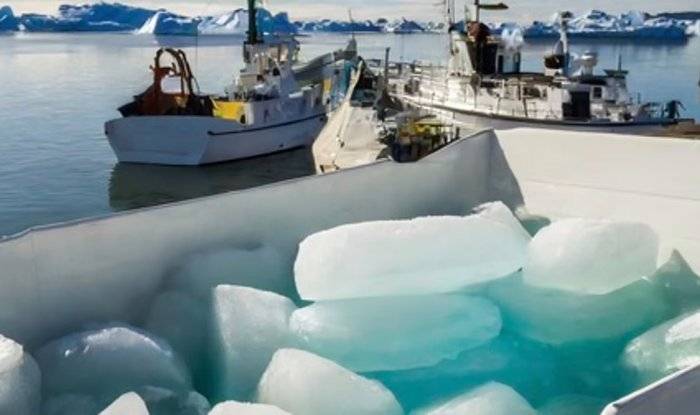
Ice from Greenland’s melting glaciers has begun to be exported to Dubai bars
Scientists have been regularly reminding us about the rapidly melting Greenland glaciers and the negative consequences for our planet’s climate for many years. But if the ancient glaciers have already started to crumble, why not at least benefit from it? Apparently, this is what the founders of the Greenlandic startup Arctic Ice have decided, and they have started supplying ice that has broken off from them to cool drinks in bars in the UAE.
The interest in Greenland ice is not accidental. According to company co-founder Malik Rasmussen, having been formed more than 100,000 years ago, it is perfectly pure – even purer than ordinary water, and there are no bubbles in it. Such purity is due to the lack of contact with pollutants associated with human activity.
French company Biomemory announced a new service for creating durable data storage based on DNA molecule. Such developments have been underway for a long time, but this is the first time that their result has become available to ordinary users. The new project is aimed at a wide audience, it is a full-fledged commercial product.
The storage device can only store textual information. The client is required to write a text, then the letters will be encoded through the sequence of four nucleotides that make up DNA. The laboratory will assemble a fragment of the molecule according to the code provided, then the substance will be dried for preservation and sealed inside a steel plate. To read the message, the vault will have to be opened, the DNA rehydrated and then sequenced.
Advertisement